Pattern of Pork Consumption in the World and Import-Export Status of Pork from India
Pork consumption patterns around the world reveal a fascinating tapestry of culinary traditions, economic factors, and cultural influences. As one of the most widely consumed meats globally, pork holds a prominent place in the diets of diverse populations, each with unique ways of preparing and enjoying it. In some regions, pork is a staple protein, deeply embedded in daily meals and traditional recipes. In others, religious or cultural taboos restrict its consumption, influencing dietary choices and food systems. This global panorama of pork consumption reflects not only varying taste preferences but also broader trends in agriculture, trade, and health. Understanding these patterns offers valuable insights into global food dynamics, highlighting how local practices and international influences shape dietary habits and food industries around the world.
World pork consumption pattern
The taste of pork is suitable to the palates of the natives of the various nations, which drives the global intake of 36% of meat consumption. This very significant portion stands for 112.6 million tons in recent year, which is estimated to grow at the pace of 2.3% year to year and expected to rise to 129 million tons by 2031. We have considered the nations those may seemed desired destination due to their ethnicity, versatility in cooking, cultural significance and logistical proximity and preferences for the Indian exports. Global average, per capita consumption of Pork meat is 38 Kg/Year. Per Capita consumption per year of the few of the nations are explained in the table hereunder to understand their dietary preferences.
Table: Per capita consumption of pork in top ten countries
Sl. No. | Country | Qnty (in MT) | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | % Change |
1 | China | 57.268 | 40.18 | 36.42 | 30.06 | 31.18 |
2 | South Korea | 2.142 | 41.37 | 38.3 | 38.01 | 8.83 |
3 | Italy | 2.064 | 34.62 | 35.58 | 33.15 | 4.43 |
4 | Vietnam | 3.219 | 32.29 | 31.51 | 26.86 | 20.22 |
5 | Russia | 4.271 | 29.34 | 28.28 | 28.12 | 4.34 |
6 | Japan | 2.823 | 22.58 | 21.83 | 21.54 | 4.83 |
7 | Mexico | 2.799 | 21.76 | 20.13 | 19.72 | 10.34 |
8 | Brazil | 3.479 | 16.54 | 15.38 | 14.45 | 14.47 |
9 | Philippines | 1.746 | 15.32 | 13.85 | 14.26 | 7.43 |
10 | Thailand | 0.934 | 13.02 | 12.98 | 12.8 | 1.72 |
Note: Consumption per capita in Kgs
Pig production and population in leading countries
In year 2023 the worldwide population of pigs were 778 million heads, that had shown a down trend from its previous year. Among the top pig producing countries China leads the world with over 434 million pigs as the data available as of April 2024. Brazil also stands out with a significant pig population of 40 to 50 million, supporting its substantial pork export market. In the European Union, countries like Germany, Spain, and France collectively contribute to a large pig population exceeding 150 million, driven by diverse production systems and strong export capabilities. Russia and Vietnam are other notable contributors, with pig populations growing due to increasing domestic and export demands. These leading countries’ production and population levels highlight their critical roles in shaping global pork supply and influencing international trade dynamics. The European Union and USA occupy the second and third position respectively with the head counts of 133 million and 75 million pigs. If China included Asia holds the largest population of 59.8% of the total Pig population of world. The pig distributions of the world are as follows: Asia -59.8%; Europe-19.5%; America-16.9%; Africa-3.3% and Oceania-0.5%.
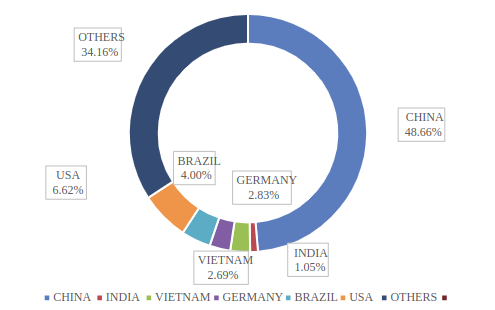
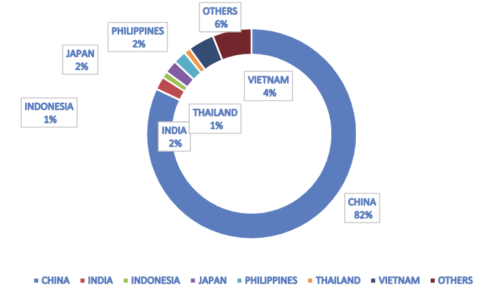
World market size and compound annual growth rate (CAGR)
The world market for pigs and pork represents a critical segment of the global food industry, characterized by its vast scale, intricate dynamics, and significant economic impact. The market encompasses a broad range of activities, from large-scale commercial pig farming to intricate global trade networks and local consumption trends. In recent years, the global market for pigs and pork has experienced notable shifts influenced by factors such as changing dietary habits, economic fluctuations, and advancements in production technology. Major pork-producing countries like China, the United States, and Brazil play pivotal roles in shaping market dynamics, while evolving consumer preferences and health considerations impact both supply and demand.
The value of the global pork market runs into hundreds of billions of dollars annually, driven by both domestic consumption and international trade. As countries adapt to emerging challenges and opportunities such as disease management, sustainability concerns, and shifting trade policies the pork market continues to evolve, reflecting broader trends in global agriculture and food security. Understanding the world market size for pigs and pork provides valuable insights into the interconnected nature of food production and consumption, highlighting the importance of this sector in addressing global dietary needs and economic stability.
Table: World market size for pork and Compound annual growth rate (CAGR)
Sl. No. | Area | REVENUE (IN Million USD) | CAGR % |
1 | Global | 3151.2 | 2.3 |
2 | North America | 1260.48 | 0.5 |
3 | Europe | 945.36 | 0.8 |
4 | Asia Pacific | 724.78 | 4.3 |
5 | South America | 157.56 | 1.7 |
6 | Middle East & Africa | 63.02 | 2 |
Note: Base Year – 2023; Forecasting Period – 2024 – 2031
World market for organic and natural pork
The world market for organic and natural pork is a niche yet rapidly expanding segment within the global meat industry. Driven by increasing consumer awareness and demand for healthier, more sustainable food options, this market is characterized by a focus on high-quality production practices. Organic pork, produced without synthetic pesticides, antibiotics, or growth hormones, and natural pork, which is minimally processed and free from artificial additives, are gaining traction among health-conscious consumers and those concerned about animal welfare. Although smaller in scale compared to conventional pork, the market for organic and natural pork is valued in the billions of dollars annually and continues to grow as consumers seek transparency and ethical practices in their food sources.
Regional trends reveal varying levels of market development. In the United States and Europe, the organic and natural pork sectors are relatively well-established, with significant consumer bases and a growing array of products available in both specialty and mainstream stores. In the US, major producers and retailers are expanding their offerings to meet rising demand, while Europe, particularly countries like Germany, France, and the UK, benefits from strong regulatory frameworks and consumer awareness. Conversely, in regions like Asia, where pork consumption is high but organic and natural products are less prevalent, the market is emerging but faces challenges related to production infrastructure and consumer education.
Despite its growth, the organic and natural pork market faces several challenges, including higher production costs, limited supply of organic feed, and complex certification processes. Prices for organic and natural pork products are typically higher than conventional options, reflecting the increased costs associated with these production methods. However, as consumer demand for sustainable and ethically produced food continues to rise, there are significant opportunities for expansion. Innovations in production techniques, improved supply chains, and increased availability of organic feed could help address these challenges and support the continued growth of the organic and natural pork market globally.
Pork exports and imports by leading countries
The global trade in pork is dominated by key exporters like the United States, the European Union, Brazil, and Canada, each contributing significantly to the global supply with exports often exceeding several million metric tons annually. The United States, with its expansive production capacity and established trade relationships, leads in exports to major markets such as China, Japan, and Mexico. The EU also plays a critical role, with substantial exports driven by countries like Spain and Germany. Brazil’s competitive pricing and production scale make it a major supplier to China and other key markets. On the import side, China is the largest buyer of pork, with imports driven by high domestic demand and periodic supply shortages, primarily sourcing from the US, EU, and Brazil. Japan, South Korea, and Mexico also play significant roles in global pork imports, relying on exports from these leading producers to meet their domestic needs. The intricate balance of global pork trade reflects a complex interplay of production capacities, trade policies, and shifting market demands.
Pork trade occupies 0.14% of total world trade. Pork is one of the most traded products of the world that held 136th position in year 2022 though between 2021 and 2022 the quantity of exports decreased from US$ 36.8 billion to 34.0 billion, a net decrease by 7.61%. The pork trade ranks 316th in the product complexity index (PCI).
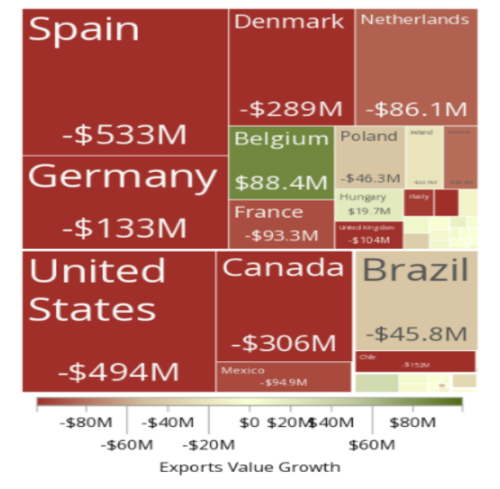
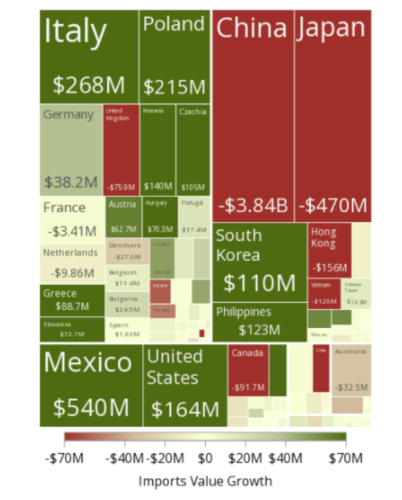
Pork export-import scenario in India
India’s pork export-import scenario is characterized by modest activity, with both exports and imports being relatively limited compared to global standards. Pork exports from India are minimal, typically focused on neighboring South Asian markets and the Middle East, reflecting the country’s smaller presence in the global pork trade. Import levels are also low, generally below 20,000 metric tons annually, with imports sourced from countries such as the United States, Canada, and the European Union to meet specific domestic demands not covered by local production. India’s pork sector faces challenges including limited production capacity, infrastructure constraints, and trade barriers, which contribute to its modest role in international pork markets. Despite these limitations, there is potential for growth as urbanization and evolving consumer preferences drive increased demand for pork, provided that improvements in production efficiency and market access are achieved.
India exported $3.75M pork in the year 2022, making it the 46th among the exporter of pork in the world. At the same year, pork was the 984th most exported product in India. The main destination of Pork exports from India are: Bhutan ($3.75M), Maldives($2.89k), and Tanzania. On the other hand, India imported $2.97M in pork in the year 2022, becoming the 112th largest importer of pork in the world. At the same year, pork was the 1019th most imported product in India. India imports pork primarily from: Belgium ($1.94M), Spain ($525k), Canada ($176k), Poland ($161k), and Brazil ($97.4k).
Conclusion
The trend of pork consumption is quite encouraging and so the market share of world trade. India being logistically very strategically located to the main consumer markets like- China, Japan, Vietnam, Philippines, Italy, Russia etc. can do tremendous and place herself very well in the list of world exporters list. Natural and sustainable pig farming with additional value addition to carbon neutrality can definitely going to create very high prospect for exports of pork from India. By resolving the challenges of quality, packaging and logistics of Indian pork, certainly India can lead the world to feed protein reach diet to the growing population.
